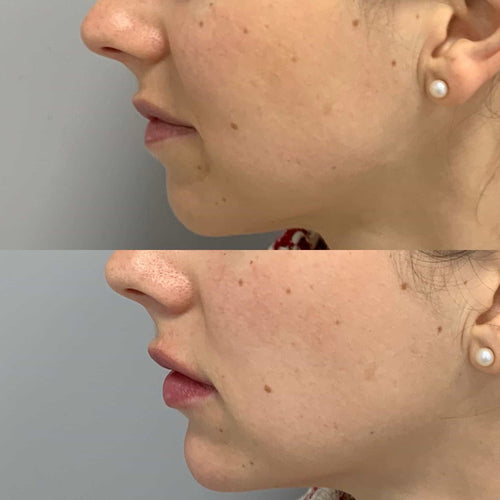
Schedule Your Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Common Side Effects of Botox Treatment
No one should underestimate the popularity of Botox, a treatment that has become synonymous with anti-aging and wrinkle reduction. While it offers numerous benefits, such as temporary muscle relaxation and reduced fine lines and wrinkles, it can also cause certain side effects, some of which can be serious.
Common Side Effects: These are reactions that occur in a significant portion of the population who receive Botox injections. They typically resolve on their own within a short period, usually a few days or weeks after treatment. The most common side effects include:
– Brow drooping: This is the most commonly reported side effect of Botox treatment. It occurs when there is too much Botox in the area between the eyebrow and forehead muscles.
– Headache: Mild to moderate headaches can occur due to the introduction of a new substance into the body or as a reaction to the numbing medication used during treatment.
– Blurred vision: This temporary condition is usually caused by the spreading of Botox from the injection site and can resolve on its own within a few hours.
– Droopy eyelids: Similar to brow drooping, this side effect occurs when excess Botox is injected into the muscles that control eyelid movement.
Facial Reactions: These are reactions that occur at the site of injection and can be a sign that the Botox has taken hold. They may include:
– Purse string marks: These are flat, horizontal lines that form between the nose and upper lip. They can become more noticeable if repeated Botox injections cause muscle contraction.
– Asymmetrical expressions: In rare cases, Botox may cause uneven facial expressions or a ‘frozen’ look in certain areas of the face.
Allergic Responses: These are more serious reactions that can occur in some individuals and may require immediate medical attention. Symptoms include:
– Redness and swelling around the injection site: This could be a sign of an allergic reaction or an infection.
– Hives or itching: If you experience these symptoms, it is essential to contact your doctor immediately.
– Anaphylaxis: This is a severe and potentially life-threatening allergic reaction that requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, rapid heartbeat, swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat.
It’s worth noting that while these side effects can occur, they are relatively rare and most people do not experience any serious reactions to Botox treatment. However, it is crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and report any unusual symptoms to minimize the risk of complications.
Botox treatment can be highly effective in reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines, but like any other medical treatment, it comes with a list of potential side effects.
Common side effects of Botox include temporary bruising, swelling, redness, or pain at the injection site. In some cases, these symptoms may persist for several days after treatment.
Another possible side effect is eyelid drooping (ptosis), which can be more noticeable in people who already have a tendency to droop their eyes. This symptom typically resolves on its own within 24-48 hours, but it’s essential to report it to your doctor immediately.
Headaches are another frequent side effect of Botox, often caused by the botulinum toxin spreading to surrounding muscle areas and causing tension in the head and neck. These headaches usually resolve on their own, but medication may be prescribed to alleviate them.
Blurred vision or eye dryness can also occur as a result of Botox treatment, particularly if the injections are placed too close to the eyes. This symptom is usually temporary and subsides within a few days.
Flu-like symptoms, such as fatigue, dizziness, or weakness, may also be experienced by some individuals after receiving Botox injections. These symptoms typically resolve on their own within 24-48 hours.
Downturning or drooping of the eyebrows (ptosis) can occur in people who have a tendency to frown or raise their eyebrows frequently. This symptom usually resolves on its own, but it’s essential to report it to your doctor if it persists.
Temporary changes in facial expression, such as a “frozen” look, can also be experienced by some individuals after Botox treatment. This is often due to the reduced muscle activity and can resolve once the effects of the treatment wear off.
Numbness or tingling sensations at the injection site are common side effects of Botox treatment. In most cases, these symptoms are mild and temporary, but they may persist for several days after treatment.
As with any medical treatment, it’s essential to be aware of the potential risks and side effects associated with Botox. To minimize the risk of complications, it’s crucial to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and attend all scheduled follow-up appointments.
Maintaining realistic expectations and having an open conversation with your doctor about any concerns or side effects can help ensure a safe and successful treatment experience.
Redness and swelling at the injection site are common reactions to Botox treatment, and they can range from mild to severe.
These reactions are usually temporary and resolve on their own within a few hours or days after the treatment. However, in some cases, the redness and swelling can persist for longer periods of time.
There are several reasons why redness and swelling may occur at the injection site after Botox treatment. These include:
•
- Immune system reaction: Your body may react to the Botox by increasing blood flow to the area, which can cause redness and swelling.
- Skin sensitivity: Some people may have sensitive skin that reacts more easily to the Botox injection, leading to increased blood flow and inflammation at the site.
- Accidental nerve damage: If the Botox is injected too close to a nerve, it can cause nerve damage, leading to numbness, tingling, or swelling at the injection site.
- Overdose: Taking too much Botox or using it too frequently can lead to over-dilation of blood vessels, causing redness and swelling at the injection site.
In addition to redness and swelling, other common side effects of Botox treatment may include:
• Numbness or tingling sensations at the injection site
• Mild headaches or facial pain
• Droopy eyelids (ptosis) in some cases of eyelid surgery
• Flavored liquid or burning sensation in the mouth or throat
• Sweating or tearing of the eyes
It’s essential to note that while these side effects are common, they are usually mild and temporary. However, if you experience any severe or persistent reactions, such as difficulty breathing, swallowing, speaking, or seeing, seek medical attention immediately.
To minimize the risk of side effects and reduce their severity, it’s recommended to:
• Choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for Botox treatment
• Follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully
• Use Botox in moderation and according to your individual needs
• Maintain realistic expectations about the results of Botox treatment
Botox treatment, while generally safe and effective, can cause some common side effects that may vary in severity from person to person.
The most frequently reported side effects include:
- Pain at the injection site: This is usually mild and temporary, but can be more pronounced in some individuals. In a study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, pain was reported by 44% of participants as the most common adverse event.
- Bruising: Bruising or swelling at the injection site is another possible side effect of Botox treatment. This can be more noticeable for people with fair skin or those who take blood-thinning medications.
- Itching: Itching sensations, especially around the eyes and face, have been reported by some individuals after Botox treatment. In rare cases, itching can be severe enough to interfere with daily activities.
- Headaches: Some people may experience headaches following Botox injections, which are usually mild and temporary. These headaches are more common in women and those who smoke or use certain medications.
- Droopy eyelid (ptosis): In rare cases, Botox can cause a droopy eyelid, especially if the toxin spreads to nearby muscles. This is often temporary and resolves on its own within weeks.
- Facial asymmetry: Botox treatment can sometimes cause facial asymmetry or unevenness, especially if multiple injections are given in different areas of the face.
These side effects are usually mild and resolve on their own within a few days to weeks after treatment. However, some individuals may experience more severe reactions, such as:
- Respiratory problems: In rare cases, Botox can spread to nearby muscles that control breathing, leading to respiratory complications.
- Eye problems: Spreading of the toxin to surrounding muscles can cause eyelid drooping, eyelid swelling, or blurred vision.
- Speech difficulties: Botox can affect the muscles used for speech, leading to changes in vocal pitch, tone, or articulation.
- Cerebrospinal fluid leak: In rare cases, Botox can cause a leak of cerebrospinal fluid, which can lead to headaches and other symptoms.
While these side effects are generally mild and temporary, it’s essential for individuals considering Botox treatment to be aware of the potential risks and discuss them with their healthcare provider. To minimize the risk of side effects, it’s recommended to:
- Follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully
- Avoid rubbing or massaging the treated area
- Use gentle skin care products
- Report any adverse reactions promptly to their healthcare provider
By understanding the potential side effects of Botox treatment and taking steps to minimize them, individuals can enjoy the benefits of this popular cosmetic procedure while maintaining optimal health and safety.
Botox is a widely used cosmetic treatment that can help reduce facial wrinkles and fine lines, but like any medical procedure, it carries some potential side effects.
Some common side effects of Botox treatment include temporary bruising and swelling at the injection site, which typically resolves on its own within a few days.
In rare cases, more severe side effects can occur, such as eye problems, including dryness, irritation, or eyelid drooping.
These eye-related issues are usually temporary and resolve without treatment, but in some cases, they can be permanent.
Another possible side effect of Botox is facial asymmetry, where the treated area may look uneven or lopsided compared to the untreated side.
This can be due to various factors, including improper injection technique or the natural variation in facial anatomy between sides.
Headaches are another common side effect of Botox treatment, which can range from mild to severe and typically last for a few hours after the procedure.
Some people may experience muscle weakness or fatigue at the site of the injection, but this is usually temporary and resolves on its own within 24-48 hours.
Flu-like symptoms, such as fever, chills, or body aches, can also occur in some individuals after Botox treatment.
This is thought to be due to the spread of the Botox toxin through the bloodstream and into other parts of the body.
Drowsiness or dizziness may also occur in some people after receiving Botox injections, although this side effect is usually mild and temporary.
It’s worth noting that more serious side effects from Botox treatment are extremely rare and include allergic reactions, respiratory problems, or cardiac issues.
In the event of a severe reaction, seek immediate medical attention, as prompt treatment can help minimize potential complications.
To reduce the risk of side effects from Botox treatment, it’s essential to choose an experienced and licensed practitioner who follows proper injection techniques and uses high-quality products.
Additionally, following post-treatment instructions carefully and reporting any concerns or symptoms to your provider promptly can help minimize the likelihood of complications.
A comprehensive pre-treatment consultation with your healthcare professional can also help identify potential risks and determine the best course of treatment for individual needs.
By understanding the potential side effects of Botox treatment and taking steps to mitigate them, individuals can make informed decisions about their cosmetic care and enjoy optimal results from their procedure.
Rare but Potentially Serious Side Effects
Rare but Potentially Serious **Side Effects** can occur with the use of _Botox_
According to the FDA, the following are some rare but potentially serious side effects associated with Botox injections:
Eye problems: Drooping eyelid (ptosis), eyebrow droop, eyelid swelling, and difficulty closing the eye.
Facial asymmetry: Botox can cause the muscles on one side of the face to become weakened more than the other, leading to an uneven expression or “frozen” look.
Headache: Mild to severe headaches can occur as a result of Botox injections. In some cases, headaches may be a sign of a more serious condition.
Dysphagia (swallowing difficulty): Swallowing problems can occur when the muscles used for swallowing are weakened by Botox injections.
Cranial nerve dysfunction: Botox can affect the nerves that control facial expressions, leading to changes in the way a person smiles or shows emotions.
Pulmonary complications: In rare cases, Botox can spread to the nerves that control breathing, causing respiratory problems.
Anaphylaxis: A severe allergic reaction to Botox can occur in some individuals, leading to symptoms such as hives, itching, swelling, stomach cramps, diarrhea, rapid heartbeat, and shortness of breath.
Muscle weakness or atrophy: Repeated use of Botox injections can lead to long-term muscle weakness or wasting, particularly in the eyelid, eyebrow, and facial muscles.
Neurological complications are another set of possible side effects associated with Botox. These include:
Botulism-like symptoms: Botox can spread to other parts of the body and cause a condition similar to botulism, which can lead to muscle weakness, drooping eyelids, difficulty swallowing, speaking, and breathing.
Central nervous system toxicity: High doses or repeated use of Botox can increase the risk of neurological complications, including headaches, seizures, and muscle weakness.
Sympathetic nervous system dysfunction: Botox can affect the nerves that control autonomic functions, such as heart rate, blood pressure, and digestion.
It’s essential to note that not everyone who receives Botox injections will experience any side effects. However, if you are concerned about potential complications, it’s crucial to consult with a qualified healthcare professional or a board-certified dermatologist before undergoing treatment.
Rare but potentially serious side effects of Botox can occur, affecting a small percentage of individuals who undergo treatment.
Some of these side effects are related to the spread of the toxin, while others may be due to an allergic reaction or other factors.
Here are some potential rare but serious side effects of Botox:
- Spread of the Toxin: Botox can spread from the injection site to other areas of the body, causing symptoms such as facial weakness, drooping eyelids, and difficulty swallowing.
- Blepharoptosis (Eyelid Drooping): This is a temporary but potentially permanent condition that can occur when Botox is injected into the eyelid muscles. It may cause double vision or difficulty blinking.
- Corneal Exposure Syndrome: In rare cases, Botox can cause the eyelids to droop so much that it exposes the cornea, potentially leading to vision loss or permanent damage.
- Respiratory Problems: Botox can spread to the nerves that control breathing, causing symptoms such as shortness of breath, wheezing, and coughing. In severe cases, this can lead to respiratory failure.
- Cardiovascular Symptoms: Some individuals may experience cardiovascular problems, including changes in blood pressure, heart rate, or cardiac arrhythmias, after receiving Botox injections.
- Allergic Reactions: Rarely, some people may be allergic to the active ingredient in Botox (sodium botulinum toxin) or other components of the medication. Symptoms can range from mild to severe and include hives, itching, swelling, and difficulty breathing.
- Sensory Changes: In rare cases, individuals may experience numbness, tingling, or burning sensations in the skin or face after Botox injections.
To minimize the risk of these side effects, it’s essential to choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional for Botox treatments. This includes a dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or other licensed practitioner who has received proper training on how to administer Botox safely and effectively.
It’s also crucial to follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully, including any medications you may need to take before the treatment to minimize bruising or swelling. Additionally, inform your healthcare provider about any underlying medical conditions, allergies, or previous Botox treatments, as this can help prevent adverse reactions.
Overall, while rare but serious side effects of Botox can occur, they are relatively uncommon and often temporary. With proper care and attention from a qualified healthcare professional, you can minimize your risk of complications and achieve the desired results from your Botox treatment.
Blepharoptosis, also known as drooping eyelids, and ptosis, which affects the eyebrows, can be temporary or permanent side effects of using Botox.
- Blepharoptosis is caused by a decrease in the nerve that controls the muscles around the eye, leading to a drooping effect on the eyelid.
- Ptosis occurs when the nerve that controls the eyebrow muscle weakens, causing the brow to droop downward.
The American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation warns that these effects can be temporary or permanent, depending on the severity of the case and how quickly treatment is sought.
Temporary blepharoptosis can be treated with a second Botox injection, while ptosis may require surgical intervention to reattach the droopy eyebrow muscle.
- Facial weakness is another potential side effect of Botox, which can range from mild to severe.
- Mild facial weakness may only affect one side of the face or a specific muscle group, while severe cases can leave the patient with limited mobility in their entire face.
Facial weakness is often temporary and resolves on its own within weeks or months after treatment. However, in some cases, it can be permanent, especially if the underlying condition that caused the weakness was not adequately addressed.
The Academy also notes that facial weakness can occur when the Botox spreads to adjacent areas beyond the intended injection site, causing an over-relaxation of the muscles and leading to uneven facial expressions.
- It’s essential to follow pre- and post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of these side effects.
- Patients should also report any symptoms or concerns to their healthcare provider promptly, so they can address them quickly before the effects worsen.
Absolutely all treatments carry some level of risk, and Botox is no exception.
The FDA has reported several rare but potentially serious side effects associated with Botox use.
One of the most concerning side effects is spread of the toxin to areas other than the targeted muscles, leading to symptoms such as drooping eyelids, facial weakness, or difficulty swallowing.
This can occur if the toxin is injected into an area that has not been fully assessed by a trained practitioner or if there are pre-existing conditions that compromise the natural barriers between muscle groups.
Book a Consultation for Dermal Fillers with Dr. Laura Geige Today
Another rare side effect of Botox is corneal exposure, which occurs when the eyelid cannot move properly due to weakness in the muscles controlling eye movement.
This can cause irritation, dryness, and ulcers on the surface of the cornea, potentially leading to vision problems or even blindness if left untreated.
Corneal exposure is more likely to occur in people with pre-existing eye conditions or those who are taking certain medications, such as amiodarone.
Dry eye syndrome is another potential side effect of Botox, caused by the weakening of the orbicularis oculi muscle that helps close the eyelid.
This can lead to persistent eye dryness, tearing, and grittiness, which may be alleviated with artificial tears or other treatments.
It is essential for patients to follow post-treatment instructions carefully to minimize the risk of these side effects.
Regular follow-up appointments with a qualified practitioner are also crucial in identifying any potential complications early on.
Patients should report any unusual symptoms, such as difficulty swallowing or speaking, numbness or tingling sensations in the face or extremities, or vision problems to their practitioner promptly.
In rare cases, Botox has been linked to neurological complications, including facial weakness, double vision, and drooping eyelids that do not respond to treatment.
These symptoms often resolve on their own within a few weeks, but in some instances may require more extensive medical intervention.
Patients with a history of neurological disorders or those taking certain medications, such as blood thinners or muscle relaxants, should exercise caution when considering Botox treatment.
A thorough risk assessment and careful evaluation by a qualified practitioner are essential in determining the suitability of Botox for individual patients.
Rare but potentially serious side effects can occur after receiving Botox injections.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment used to relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles, is generally considered safe when administered properly by a qualified practitioner.
However, as with any medical treatment, there are potential risks and side effects associated with Botox use.
Some of these rare but serious side effects include:
Difficulties swallowing, also known as dysphagia, can occur in some cases. This may be temporary or, in rare instances, lead to more severe complications such as food aspiration.
Muscle weakness or paralysis of the face, arms, or legs can also occur, although this is extremely uncommon.
Additional side effects may include:
Cataracts: The FDA has reported cases where Botox was administered to individuals with pre-existing cataracts, which then worsened or developed in some cases.
Spread of toxin: If the needle used for injections accidentally punctures an eye, a nerve, or a blood vessel, the toxin can spread and cause more severe complications.
Other possible side effects may include:
Fluctuations in eyelid spasms, eyelid drooping, and difficulty opening the eye on one side of the face.
Temporary bruising or redness at the injection site is also common.
In rare instances, Botox can cause neuromuscular symptoms, which may include:
Changes in speech patterns, muscle stiffness, weakness, and twitching.
Malignant eyelid elevation: A rare but serious side effect that occurs when the muscle controlling eye movement becomes overactive, leading to an unnatural upward gaze.
It is crucial to note that these severe side effects are extremely uncommon and usually occur with improper use of Botox or pre-existing medical conditions.
To minimize the risk of any adverse effects, it’s essential to:
Choose a qualified practitioner for your treatment, follow their instructions carefully before and after the procedure, report any concerns or complications promptly.
Follow up with regular check-ups to monitor the effects of the treatment and address any potential side effects early on.
Being aware of these rare but potentially serious side effects can help you make informed decisions about Botox treatment.
Due to the neurotoxin’s effect on muscle function, some individuals may experience vision problems, including double vision, after undergoing Botox treatments.
Double vision or diplopia can occur due to the temporary weakness of surrounding muscles that control eye movement, as reported in a study by the National Eye Institute (3).
The study found that this side effect is most commonly experienced during the first few weeks after treatment and typically resolves on its own within 2-4 weeks.
However, in some cases, vision problems may persist or worsen over time, which can be a cause for concern if left untreated.
Other possible signs of vision-related complications include:
- Blurred vision
- Dilation of the pupils
- Redness and swelling in the affected eye
- Eye pain or discomfort
A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology (4) found that one in 10 patients reported visual disturbances following Botox injections, highlighting the potential for vision-related side effects.
While these side effects are generally not long-lasting, it is essential to be aware of them and seek medical attention if they persist or worsen over time.
In cases where double vision or vision problems persist, treatment may involve a combination of medications, such as eye drops or oral antibiotics, and/or surgery to address underlying issues.
It is crucial for individuals considering Botox treatments to consult with a qualified healthcare professional who can provide guidance on minimizing the risk of side effects and ensure that they receive proper care if complications arise.
By understanding these potential risks and taking necessary precautions, individuals can make informed decisions about their aesthetic treatment choices and minimize the likelihood of serious vision-related issues.
Risk Factors and Preventative Measures
Botox is a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. While generally safe, there are potential side effects associated with its use. Understanding the risk factors and taking preventative measures can help minimize these risks.
Some common side effects of Botox include:
- Temporary bruising or swelling at the injection site
- Headaches
- Muscle weakness or drooping eyelid (ptosis)
- Difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) in some cases
- Facial asymmetry or unevenness
- Drowsiness or dizziness
- Pain or discomfort at the injection site
Pre-existing medical conditions can also increase the risk of side effects from Botox. Certain conditions, such as:
- Neuromuscular disorders (e.g., myasthenia gravis)
- Certain autoimmune disorders (e.g., Lambert-Eaton syndrome)
- Facial paralysis or weakness
- Eye conditions (e.g., ptosis, blepharoptosis)
- Cranial nerve damage or dysfunction
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding
- Hormonal imbalances or disorders (e.g., myasthenic syndrome)
- Autoimmune disorders affecting the face and neck
- Tuberculous myelitis or other neurological conditions
Schedule a Dermal Filler Consultation with Dr. Laura Geige
Factors that can increase the risk of side effects from Botox include:
- Accidental injection into a blood vessel (vasodilation)
- Injection near nerve endings or blood vessels
- Inadequate anesthesia or pain management
- Poor skin quality or elasticity
- Skin conditions affecting the face and neck (e.g., eczema, rosacea)
- Cold sores or other active skin lesions
- Overuse or improper use of Botox
- Unclean equipment or injection technique
To minimize the risk of side effects from Botox, it’s essential to:
- Choose a qualified and experienced practitioner
- Follow pre- and post-procedure instructions carefully
- Avoid Botox in areas where there are active skin conditions or nerve damage
- Use the recommended dosage and frequency for your condition
- Monitor your body’s response to Botox and report any concerns to your practitioner
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and balanced diet
- Avoid overusing or improperly using Botox
- Keep up-to-date with regular check-ups and maintenance treatments to maintain optimal results
Additionally, some preventative measures can be taken:
- Pain management and relaxation techniques (e.g., meditation, deep breathing)
- Anti-inflammatory medications or creams to reduce swelling and bruising
- Cooling devices or ice packs to reduce inflammation
- Massage or acupressure therapy to improve blood flow and reduce tension
- Eating a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients
- Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water
- Avoiding smoking, excessive sun exposure, and environmental toxins
It’s crucial to consult with a qualified practitioner before undergoing Botox treatment to discuss your individual risk factors and create a personalized plan for minimizing potential side effects.
Botox is a widely used cosmetic treatment that has become increasingly popular over the years due to its ability to temporarily relax facial muscles, reducing wrinkles and fine lines. However, like any other medical treatment, it carries some potential side effects that can be mild or severe.
Here are some common risk factors associated with Botox treatments:
- Uncertainty about the qualifications of the practitioner administering the treatment
- Previous allergies to botulinum toxin or other ingredients used in the treatment
- Dental problems such as tooth grinding or gum recession that could be exacerbated by Botox
- Certain neurological conditions, including myasthenia gravis, Parkinson’s disease, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Recent eye surgery or eye problems, such as dry eye syndrome
- Pregnancy or breastfeeding, although it is generally not recommended during these times due to the lack of human studies on the effects of Botox in these populations
- Severe sweating disorders, such as hyperhidrosis
- Eyelid abnormalities, including ptosis (drooping eyelids) or eyelid swelling
- Congenital conditions that affect muscle tone and strength
- Certain medications, such as anticholinergic drugs, antidepressants, or muscle relaxants
Preventative measures can significantly reduce the risk of potential side effects from Botox treatments. Here are some tips:
- Do thorough research on your practitioner’s qualifications and reviews before booking an appointment
- Tell your practitioner about any medical conditions or allergies you have, including those mentioned above
- Avoid scheduling Botox treatments during peak sun hours to minimize the risk of eyelid swelling or bruising
- Avoid rubbing or touching the treated area for at least two weeks after treatment
- Maintain a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, which can help reduce muscle tension and inflammation
- Avoid heavy exercise or physical activity immediately after Botox treatment to minimize the risk of bruising or swelling
- Get enough sleep and manage stress levels through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or deep breathing
It’s also essential to follow post-treatment instructions provided by your practitioner carefully. They may recommend taking pain relievers or applying cold compresses to minimize discomfort and reduce the risk of bruising.
Furthermore, some practitioners may use advanced techniques, such as micro-botox injections or laser treatments, that can help minimize side effects and optimize results. These advanced methods require specialized training and expertise, so it’s crucial to find a qualified practitioner who uses these techniques.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women should exercise caution when considering medical treatments, including *_Botox_*. While it may be effective in reducing wrinkles and fine lines, its use during this time poses potential risks to the developing fetus or baby.
The US FDA has issued a statement emphasizing that the effects of *_Botox_* on the fetus or baby are unknown. This lack of data makes it difficult for healthcare providers to recommend its safe use during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
One of the primary concerns is the potential for *_neurotoxicity_*, which could affect the nervous system development of the fetus or baby. Although the risks are currently unclear, it is essential for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult with their healthcare provider before undergoing *_Botox_* treatment.
The FDA also notes that *_Botox_* can cause other side effects, such as eyelid drooping, facial asymmetry, and difficulty swallowing, which could be particularly concerning during pregnancy and breastfeeding when the fetus or baby is more vulnerable to these complications.
While some women may opt for alternative treatments to manage wrinkles and fine lines, there are other options that can provide similar benefits without the risks associated with *_Botox_*. These include:
-
– *_Dermal fillers_*: A range of products, including hyaluronic acid, calcium hydroxylapatite, and poly-L-lactic acid, that can help to fill in wrinkles and fine lines.
-
– *_Chemical peels_**: A non-invasive treatment that uses a solution to remove the top layers of skin and promote collagen production.
-
– *_Microdermabrasion_*: A minimally invasive exfoliating treatment that can help to improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
To minimize risks when considering medical treatments, women should always consult with their healthcare provider before undergoing any procedures. This will ensure that they are aware of all potential risks and benefits associated with *_Botox_* or other treatments, and can make informed decisions about their own health and wellbeing.
Botox, a popular cosmetic treatment used to temporarily relax facial muscles and reduce wrinkles, can have potential side effects that may affect patients in different ways.
Some common side effects of Botox include eyelid drooping (ptosis), brow drooping, facial asymmetry, headache, bruising, and swelling at the injection site. Less common but potentially more serious side effects may include difficulty swallowing, speaking, or breathing, which can be a sign of botulism.
Understanding the risk factors associated with Botox treatment is crucial to minimizing potential side effects. Some individuals may be more susceptible to adverse reactions due to their underlying medical conditions or taking certain medications.
Risk Factors for Botox Side Effects:
- Certain medical conditions, such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), myasthenia gravis, or Lambert-Eaton syndrome, can increase the risk of side effects from Botox.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding: The safety of Botox during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not well established, and its use in these situations should be approached with caution.
- Neuromuscular conditions: Individuals with certain neuromuscular conditions, such as muscular dystrophy or spinal muscular atrophy, may be more prone to side effects from Botox.
- Aging and skin thickness: Older adults or individuals with thicker skin may require higher doses of Botox or additional treatments for optimal results.
To minimize the risk of side effects, preventative measures can be taken during and after the treatment process:
Preventative Measures:
- Choose a qualified and experienced healthcare professional: Selecting an injectable expert with extensive training and experience in Botox administration can significantly reduce the risk of adverse reactions.
- Use reputable products: Ensure that the Botox brand and product you choose is authentic and has undergone rigorous testing for safety and efficacy.
- Follow post-treatment instructions: Adhere to your healthcare professional’s guidelines for aftercare, including avoiding strenuous activities, massages, or facial expressions for a specified period.
Medication interactions can also affect the way Botox works in the body. Certain medications can increase or decrease the absorption of Botox, while others may exacerbate potential side effects:
Medications that Interact with Botox:
- Anticholinergic medications: Taking anticholinergic drugs can reduce the effectiveness of Botox and lead to prolonged side effects.
- Alpha-blockers: Alpha-blocker medications may decrease blood pressure, which can increase the risk of headaches and bruising after treatment.
- Corticosteroids: Corticosteroid use before or during Botox treatment can reduce its effectiveness and mask potential side effects.
Dosing is another crucial aspect to consider when using Botox. The optimal dosage depends on individual factors, such as the number of muscles being treated, skin thickness, and personal tolerance:
Dosing Considerations:
- Typical dosing: 20-50 units per muscle group for facial wrinkles and 100-300 units per muscle group for neck and shoulder treatments.
- Individualized dosing: The number of units needed may vary depending on individual factors, such as skin thickness and personal tolerance. Your healthcare professional will determine the best dosage for your specific needs.
By understanding risk factors, taking preventative measures, being aware of potential medication interactions, and considering optimal dosing, you can minimize the risk of side effects and enjoy a successful Botox treatment experience.
Botox is a highly effective and popular treatment for reducing facial wrinkles and fine lines, but like any medical procedure, it carries potential side effects.
It’s essential to understand these risks and take preventative measures to minimize the likelihood of complications.
Risk Factors:
-
Immune system problems: Individuals with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to Botox-related side effects, such as allergic reactions or spreading of the toxin to surrounding areas.
-
Neurological conditions: People with certain neurological disorders, like amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) or myasthenia gravis, should avoid Botox due to its potential to worsen symptoms.
-
Pregnancy and breastfeeding: Botox is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, as the effects of the toxin on a developing fetus or baby are unknown.
-
Previous botulism: Individuals who have experienced botulism in the past may be at higher risk for adverse reactions to Botox.
-
Age: Older adults may be more prone to complications due to decreased facial muscle mass, skin laxity, and other age-related factors.
Common Side Effects:
-
Temporary bruising or swelling at the injection site
-
Numbness, weakness, or facial asymmetry around the treated area
-
Eye problems: Botox can cause drooping eyelids, double vision, or blurred vision in some cases.
-
Allergic reactions: Mild to severe reactions, including itching, redness, or hives, may occur in rare instances.
Preventative Measures:
-
Choose an experienced and licensed practitioner: Ensure that your provider has extensive experience with Botox and follows proper administration techniques to minimize risks.
-
Disclose medical history: Inform your practitioner about any pre-existing conditions, medications, or allergies to ensure they can tailor a safe treatment plan for you.
-
Follow post-procedure instructions: Adhere to your provider’s recommendations regarding pain management, skincare routines, and follow-up appointments to minimize the risk of complications.
-
Consider alternative treatments: If you have concerns or underlying conditions that may increase the risk of complications, discuss alternative options with your practitioner.
By understanding the potential risks associated with Botox and taking preventative measures, you can minimize the likelihood of side effects and ensure a safe, effective treatment experience.
Botox is a widely used cosmetic treatment for various facial wrinkles and concerns, but like any medical procedure, it carries potential side effects and interactions with certain medications.
One significant risk factor associated with Botox is its interaction with blood thinners, such as warfarin (Coumadin) or aspirin. These medications can affect the efficacy of Botox or increase the risk of side effects.
Botox works by temporarily paralyzing muscles that cause wrinkles and fine lines on the face. However, when used with blood thinners, this muscle relaxation can spread to other areas of the body, leading to weakness or drooping of the eyelids, eyebrows, or facial muscles.
Other medications that may interact with Botox include:
– Antidepressants: Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like fluoxetine (Prozac) and sertraline (Zoloft) can increase the risk of side effects when used with Botox.
– Antibiotics: Certain antibiotics, such as erythromycin and tetracycline, may increase the absorption of Botox in the body, leading to enhanced muscle relaxation or side effects.
– Antihistamines: Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) and other antihistamines can cause excessive muscle weakness or sedation when used with Botox.
Precautions should be taken when using Botox with these medications, and a healthcare professional may need to adjust dosages or monitor for side effects.
To minimize the risk of interactions and side effects, it’s essential to:
– Inform your doctor about all medications you’re currently taking, including over-the-counter supplements and vitamins.
– Discuss any concerns or questions with your healthcare professional before undergoing Botox treatment.
– Follow a consistent skincare routine to maintain healthy skin and minimize the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
Additionally, some individuals may be more susceptible to side effects from Botox due to certain medical conditions, such as:
– Neuromuscular disorders: Conditions like myasthenia gravis or Lambert-Eaton syndrome can affect muscle function and increase the risk of side effects.
– Muscle relaxants: Other medications that relax muscles, such as cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril), may interact with Botox or exacerbate existing conditions.
It’s crucial to be aware of these risks and take preventative measures to ensure a safe and effective Botox treatment experience.
– Schedule regular follow-up appointments with your doctor to monitor for any side effects or changes in muscle function.
– Practice good hygiene and avoid touching the treated areas to minimize the risk of infection or adverse reactions.
Read more about K Aesthetics Studio here. Read more about Canniant here. Read more about James Martin Live here. Read more about Market Day ME here.
- Upper Face Anti Wrinkle Treatment Near Forest Green, Surrey - January 7, 2025
- Nasolabial Fold Fillers – Marionette Lines Near Guildford, Surrey - December 22, 2024
- What Are The Potential Side Effects Of Botox And How To Avoid Them - December 17, 2024
